A Comprehensive Guide to Different Types of PET/CT Scanners
Discover the essential role of PET/CT scanners in modern medical diagnostics. Learn about standalone PET and CT scanners, hybrid PET/CT systems, and specialized mobile and cardiac PET/CT scanners. These advanced imaging technologies are crucial for detecting and managing conditions such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders, providing healthcare professionals with the tools needed for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Standalone PET Scanners
Standalone PET scanners are designed to capture metabolic processes within the body. By using a radioactive tracer, these scanners provide detailed images of how tissues and organs are functioning. They are particularly effective in identifying cancerous cells, as these cells often have higher metabolic rates than normal cells.


Standalone CT Scanners
Computed Tomography (CT) scanners use X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. These scans are highly effective for visualizing the structure of bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues. CT scans are commonly used in emergency rooms to quickly diagnose traumatic injuries.
Hybrid PET/CT Scanners
Hybrid PET/CT scanners combine the functional imaging capabilities of PET with the anatomical detail provided by CT. This integration allows for more precise localization of abnormalities, enhancing diagnostic accuracy. Hybrid scanners are widely used in oncology for tumor detection, staging, and monitoring treatment response.
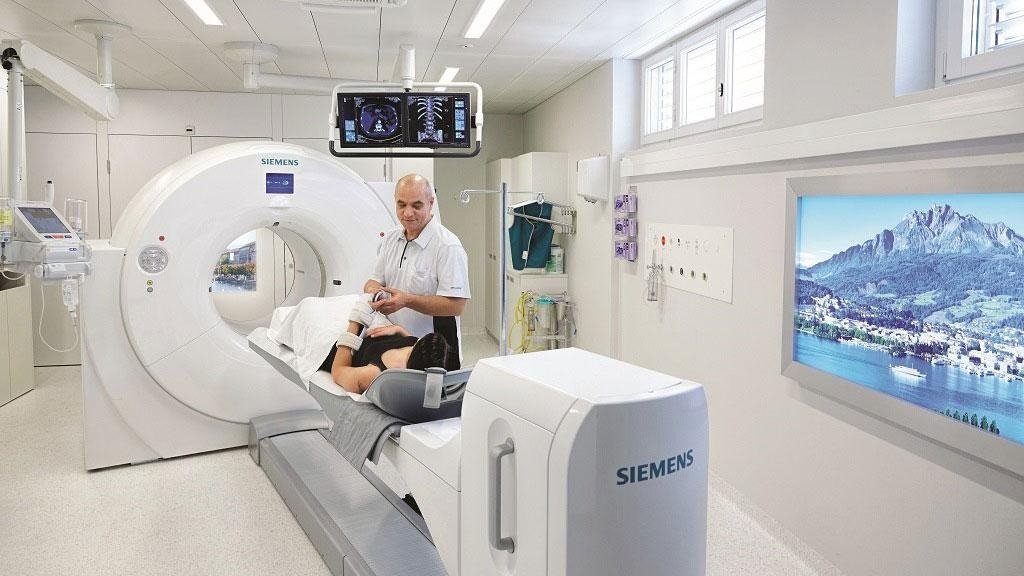
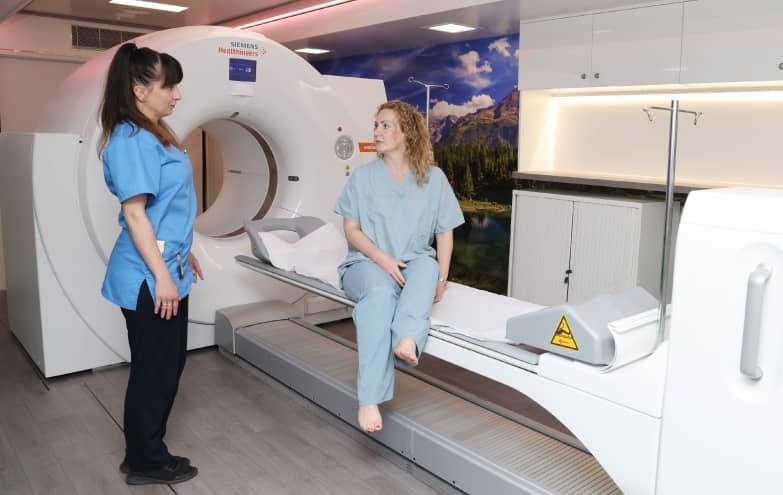
Mobile PET/CT Scanners
Mobile PET/CT scanners offer the flexibility of bringing advanced imaging technology to various locations, including remote or underserved areas. These portable units provide similar diagnostic capabilities as stationary scanners, making them invaluable for community health outreach programs and temporary medical facilities.
Dedicated Cardiac PET/CT Scanners
Dedicated cardiac PET/CT scanners are specialized for cardiovascular imaging. They provide detailed images of the heart, enabling the assessment of coronary artery disease, myocardial perfusion, and viability. These scanners are essential for cardiologists in planning and evaluating treatments for heart conditions.

Conclusion
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Computed Tomography (CT) scanners are crucial tools in modern medical diagnostics. These imaging technologies help in detecting and managing various medical conditions, including cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders. Understanding the different types of PET/CT scanners can aid healthcare professionals in selecting the most appropriate imaging solution for their needs.
